[heap] 힙 이란? (feat.cpp)

힙 이란?
완전 이진트리로 구현되어 있으며 속성에 따라 부모 노드에 큰 값, 작은 값 둘 중 하나가 올 수 있습니다.
최대 힙 : 자식 노드보다 부모 노드의 값이 큰 힙을 뜻 합니다.
최소 힙 : 자식 노드보다 부모 노드의 값이 작은 힙을 뜻 합니다.
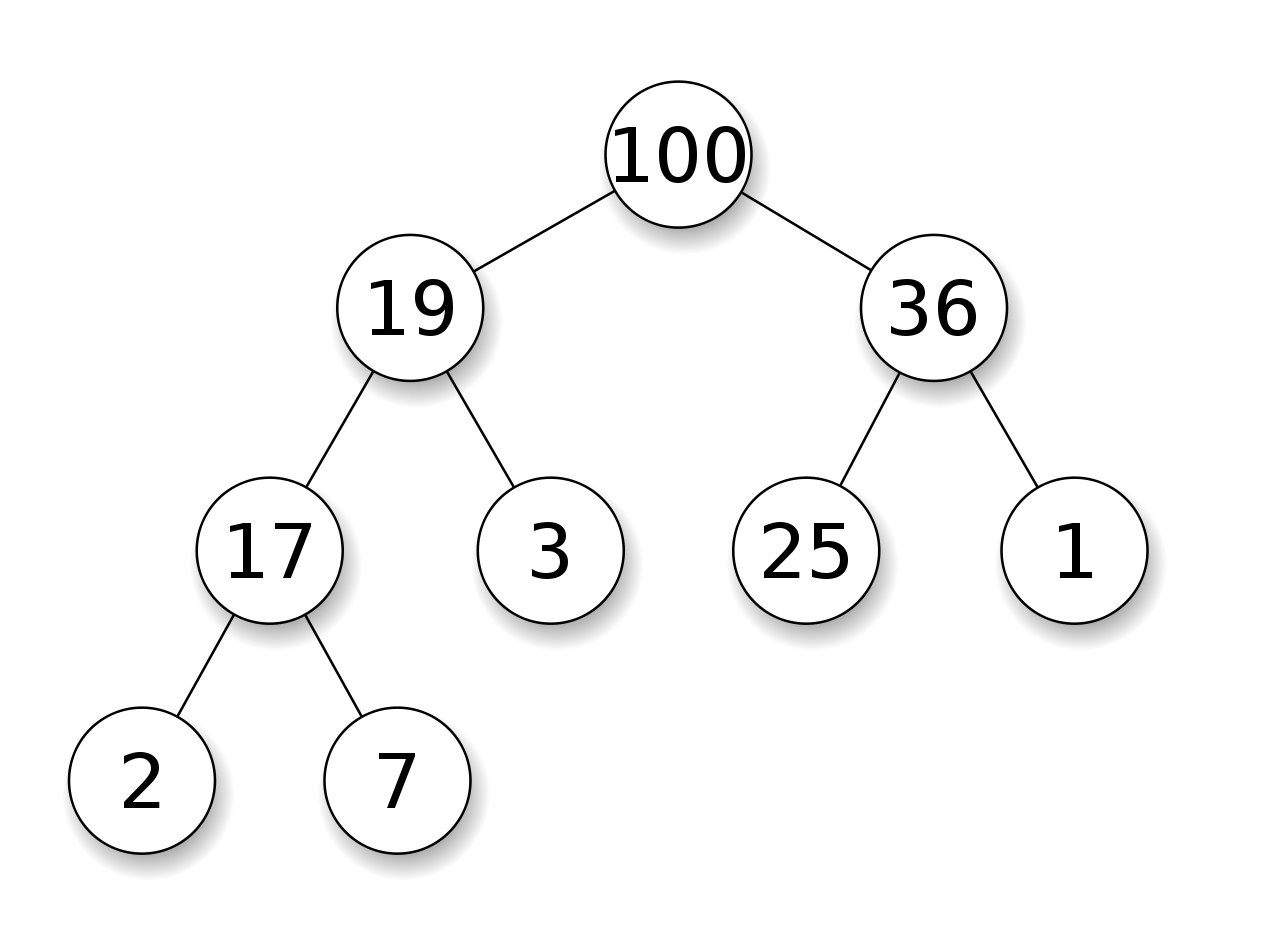
힙은 반환 시 최대 값 또는 최소 값을 반환합니다.
즉 위의 트리에서 루트 노드(최상위 노드)가 반환 후 재 정렬하여 루트 노드에 최대 값 또는 최소 값을 배치시킵니다.
구현 (최대 힙) - 배열
1. PUSH()
데이터를 힙에 저장하는 작업입니다.
트리를 배열로 생각해 봅니다.
완전 이진트리는 부모 노드 아래에 자식 노드 두 개가 있는 구조입니다.
즉, 자식 / 2의 값이 부모 노드의 인덱스가 됩니다.
void push(int data){
heap[++index] = data;
int child = index;
int parent = child / 2;
...
}
데이터를 저장하기만 하고 끝내면 힙이 되지 않습니다.
최대 힙을 구현하는 것이기 때문에 들어온 값과 상위 노드 값들과 비교하며 정렬을 해줍니다.
정렬 방식은 부모 노드와 자식 노드를 비교하여 자식 노드가 더 클 시 자리를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복하며 루트 노드까지 반복하여 비교해갑니다.
void push(int data){
...
while(child > 1 && heap[child] > heap[parent]){
swap(heap[parent], heap[child]);
// 노드를 타고 올라간다.
child = parent;
parent = child / 2;
}
}
2. POP()
데이터를 꺼내는 작업입니다. (루트 노드 출력)
루트 노드 값을 지우는 방법은 루트 노드 값과 Index에 위치한 값과 자리를 변경합니다.
그 후 index에 값을 0으로 변경합니다.
int pop(){
// 루트 노드값 저장
int ret = heap[1];
// 루트 노드 값 삭제
swap(heap[1], heap[index]);
heap[index] = 0;
--index;
...
return ret;
}
pop() 작업도 push() 작업과 동일하게 재 정렬을 해서 루트 노드에 최대 값이 오도록 해줍니다.
여기서 생각해봐야 할 것은 자식 노드는 두 개입니다.
그렇다면 자식 노드가 두 개인 경우 자식 노드 안의 값이 더 큰 쪽으로 child 값을 지정해 줍니다.
어느 자식의 길로 갈지 정해준다 생각하면 됩니다.
int pop(){
...
int parent = 1;
int child = parent * 2;
// 자식 노드가 2개 라면 (child : 첫번째 자식, child + 1 : 두번째 자식)
if(child + 1 <= index)
child = heap[child] > heap[child + 1] ? child : child + 1;
...
}
어느 자식 쪽으로 갈지 정했으면 현재 값이 들어있는 노드(index)까지 부모와 자식을 비교해서 자식이 크면 부모 위치로 변경해주는 작업을 반복해줍니다.
int pop(){
...
while(child <= index && heap[parent] < heap[child]){
swap(heap[parent], heap[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2;
if(child + 1 <= index)
child = heap[child] > heap[child + 1] ? child : child + 1;
}
...
}
전체 코드
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 256
using namespace std;
int heap[MAX_SIZE];
int index = 0;
void swap(int & a, int & b){
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
void push(int data){
heap[++index] = data;
int child = index;
int parent = child / 2;
while(child > 1 && heap[parent] < heap[child]){
swap(heap[parent], heap[child]);
child = parent;
parent = child / 2;
}
}
int pop(){
int ret = heap[1];
swap(heap[1], heap[index]);
heap[index--] = 0;
int parent = 1;
int child = parent * 2;
if(child + 1 <= index){
child = (heap[child] > heap[child + 1]) ? child : child + 1;
}
while(child <= index && heap[parent] < heap[child]){
swap(heap[parent], heap[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2;
if(child + 1 <= index){
child = (heap[child] > heap[child + 1]) ? child : child + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
테스트 코드 (필요하신 분만)
1 : push() 작업
2 : pop() 작업
3 : 현재 배열 안에 상태를 확인할 수 있습니다.
int main()
{
while (true)
{
int choice = 0;
int push_data = 0;
cout << "input : ";
cin >> choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
cout << "push : ";
cin >> push_data;
push(push_data);
break;
case 2:
cout << pop() << endl;
break;
case 3:
for (int i = 1; i < MAX_HEAP_SIZE; ++i)
{
if (heap[i] == 0)
break;
cout << heap[i] << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "================================" << endl;
break;
default:
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}

'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 트라이 알고리즘이란 ? (feat.cpp) (0) | 2020.11.03 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스] 위장 (0) | 2020.11.02 |
| [프로그래머스] 가장 큰 수 (0) | 2020.10.30 |
| [프로그래머스] 괄호 변환 (0) | 2020.10.29 |
| [프로그래머스] 소수 찾기 (0) | 2020.10.28 |
